Must Know
-
The stack grows towards lower addresses, and at the end there are typically two instructions:
leaveretleaveis equivalent to the following, which sets up RBP to pop off RIP:
mov rsp, rbppop rbpretpops the RIP off and the CPU jumps to return to wherever it was, roughly:
pop rip -
Calling conventions for x86 (required for 32 bit ROP w/parameters):
- Arguments are passed on the stack, pushed right to left (last argument pushed first)
- Push arguments starting with the last argument to the first argument
push ARG_Cpush ARG_Bpush ARG_Acall function -
Calling conventions for x86_64 (required for 64 bit ROP w/parameters):
- Arguments 1-6 are passed via registers RDI, RSI, RDX, RCX, R8, R9 respectively
- Arguments 7 and above are pushed on to the stack.
Helpful Diagrams
Relative addressing within a function to RBP:
[RBP+8] → return address[RBP] → saved old RBP[RBP-8] → first local variable[RBP-16] → second local variable...Sample stack frame in memory:
0x7fffffffe0c8 : return address0x7fffffffe0c0 : saved RBP0x7fffffffe0b8 : local variable a0x7fffffffe0b0 : local variable b0x7fffffffe0a8 : local variable c0x7fffffffe0a0 : local variable d0x7fffffffe098 : RSP (bottom of frame)Stack Frame for a Sample ROP Chain:
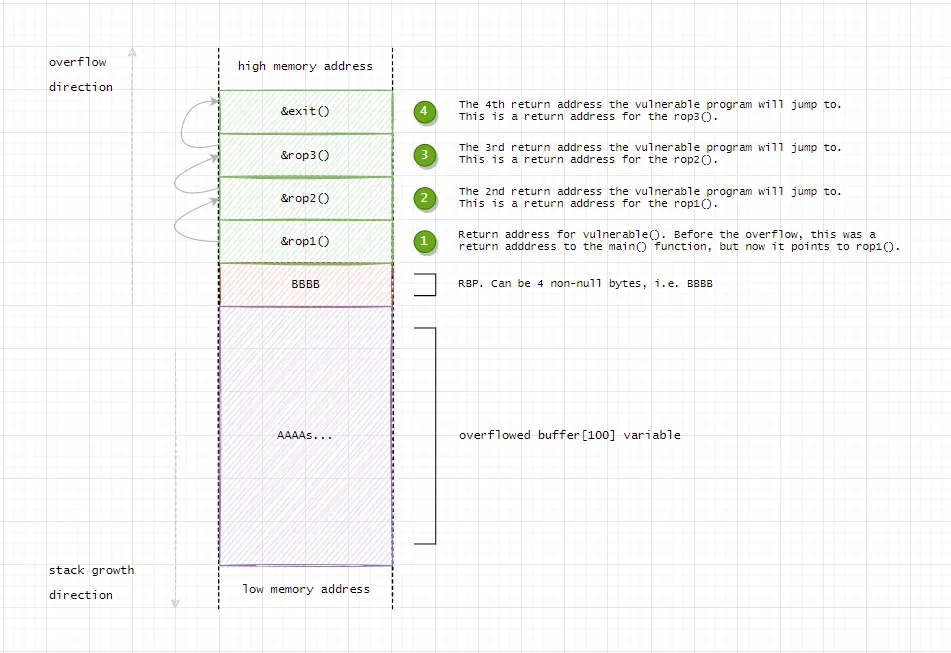
Helpful Resources
- pwntools cheatsheet
- Exploit Dev roadmap
- VR in the Real World part 2 and part 3
- x86_64 syscalls